Ethiopia
| Part of | East Africa |
|---|---|
| Year dem found am | 21 August 1995 |
| Official name | la République démocratique fédérale d’Éthiopie |
| Native label | የኢትዮጵያ ፌዴራላዊ ዲሞክራሲያዊ ሪፐብሊክ, Federaalawaa Dimokraatawaa Repabliikii Itoophiyaa, ናይኢትዮጵያ ፌዴራላዊ ዴሞክራሲያዊ ሪፐብሊክ |
| Short name | 🇪🇹 |
| IPA transcription | ɛtɪˈuːpɪɑ |
| Official language | Amharic |
| Anthem | March Forward, Dear Mother Ethiopia |
| Culture | culture of Ethiopia |
| Motto text | Land of origins, Gwlad y tarddu |
| Continent | Africa |
| Country | Ethiopia |
| Capital | Addis Ababa |
| Located in time zone | UTC+03:00, East Africa Time, Africa/Asmara |
| Located in/on physical feature | East Africa |
| Coordinate location | 9°0′0″N 40°0′0″E |
| Coordinates of easternmost point | 8°0′4″N 48°0′3″E |
| Coordinates of northernmost point | 14°52′48″N 37°54′0″E |
| Coordinates of southernmost point | 3°24′14″N 39°33′9″E |
| Coordinates of westernmost point | 7°56′41″N 32°59′53″E |
| Highest point | Ras Dashen |
| Lowest point | Danakil Depression |
| Government ein basic form | federal republic |
| Office held by head of state | President of Ethiopia |
| State ein head | Taye Atske Selassie |
| Office head of government hold | Prime Minister of Ethiopia |
| Government ein head | Abiy Ahmed Ali |
| Executive body | Government of Ethiopia |
| Legislative body | Federal Parliamentary Assembly |
| Central bank | National Bank of Ethiopia |
| Currency | bir |
| Driving side | right |
| Hashtag | Ethiopia |
| Top-level Internet domain | .et |
| Flag | Flag of Ethiopia |
| Coat of arms | Emblem of Ethiopia |
| Geography of topic | geography of Ethiopia |
| Get characteristic | not-free country |
| History of topic | history of Ethiopia |
| Patron saint | Saint George |
| Economy of topic | economy of Ethiopia |
| Demographics of topic | demographics of Ethiopia |
| Mobile country code | 636 |
| Country calling code | +251 |
| Trunk prefix | 0 |
| Emergency phone number | 911, 907, 939, 991 |
| Licence plate code | ETH |
| Maritime identification digits | 624 |
| Category for maps or plans | Category:Maps of Ethiopia |

Ethiopia, alias Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, be landlocked country. Edey Africa ein horn insyd. Ein den Eritrea dey share border for north, den plus Djibouti for northeast, Somalia for de east den northeast, Kenya for de south, South Sudan for de west, den Sudan for de northwest. Ethiopia dey cover land area of 1,112,000 square kilometres (472,000 sq. miles).[1] As of 2023, ebe home to around 128 million inhabitants, wey dey make am de 13th-most populous country for de world insyd, de 2nd-most populous insyd Africa after Nigeria, den de most populated landlocked country for Earth top.[2][3] De national capital den largest city, Addis Ababa, dey lie several kilometres west of de East African Rift wey dey split de country into de African den Somali tectonic plates.[4]
Ethiopia be multi-ethnic state plus ova 80 different ethnic groups. Christianity be de most widely faith dem profess insyd de country, plus significant minorities of de adherents of Islam den small percentage to traditional faiths. Dis sovereign state be founding member of de UN, de Group of 24, de Non-Aligned Movement, de Group of 77, den de Organisation of African Unity. Addis Ababa be de headquarters of de African Union, de Pan African Chamber of Commerce and Industry, de United Nations Economic Commission for Africa, de African Standby Force den chaw of de global non-governmental organizations wey dey focus for Africa top. Ethiopia cam turn full member of BRICS insyd 2024.[5]
Government den politics
Administrative divisions
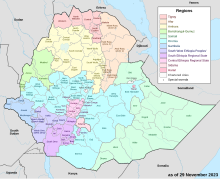
Ethiopia be administratively divided go four levels: regions, zones, woredas (districts) den kebele (wards). De country dey comprise 12 regions den two city administrations under dese regions, plenty of zones, woredas den neighbourhood administration: kebeles. De two federal-level city administrations be Addis Ababa den Dire Dawa.
Demographics
| Ethnic groups insyd Ethiopia | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ethnic group | Population | ||
| Oromo | 25.4 (34.4%) | ||
| Amhara | 19.9 (27.0%) | ||
| Somali | 4.59 (6.2%) | ||
| Tigrayans | 4.49 (6.1%) | ||
| Sidama | 2.95 (4.0%) | ||
| Gurage | 1.86 (2.5%) | ||
| Welayta | 1.68 (2.3%) | ||
| Afar | 1.28 (1.7%) | ||
| Hadiya | 1.27 (1.7%) | ||
| Gamo | 1.10 (1.5%) | ||
| Others | 9.30 (12.6%) | ||
| Population insyd millions according to 2007 Census[6] | |||
Urbanization
| Largest cities anaa towns insyd Ethiopia
CSA (Urban population projection values of 2016)[7] | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Name | Region | Pop. | Rank | Name | Region | Pop. |
| 1 | Addis Ababa | Addis Ababa | 3,352,000 | 11 | Shashamane | Oromia | 154,587 |
| 2 | Gondar | Amhara | 341,991 | 12 | Bishoftu | Oromia | 153,847 |
| 3 | Mek'ele | Tigray | 340,858 | 13 | Sodo | SNNPR | 253,322 |
| 4 | Adama | Oromia | 338,940 | 14 | Arba Minch | SNNPR | 151,013 |
| 5 | Hawassa | SNNPR | 318,618 | 15 | Hosaena | SNNPR | 141,352 |
| 6 | Bahir Dar | Amhara | 297,794 | 16 | Harar | Harari | 133,000 |
| 7 | Dire Dawa | Dire Dawa | 285,000 | 17 | Dila | SNNPR | 119,276 |
| 8 | Dessie | Amhara | 198,428 | 18 | Nekemte | Oromia | 115,741 |
| 9 | Jimma | Oromia | 186,148 | 19 | Debre Birhan | Amhara | 107,827 |
| 10 | Jijiga | Somali | 164,321 | 20 | Asella | Oromia | 103,522 |
References
- ↑ Ethiopia EO (30 July 2023). "About Ethiopia". Embassy Of Ethiopia Washington.
- ↑ "Population Projections for Ethiopia 2007–2037". www.csa.gov.et. Archived from the original on 3 August 2020. Retrieved 25 September 2020.
- ↑ "Ethiopia". The World Factbook (2024 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 24 September 2022. (Archived 2022 edition.)
- ↑ "Ethiopia". The World Factbook. CIA. Retrieved 5 April 2021.
- ↑ "Egypt, Iran, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Ethiopia formally join BRICS". Daily News Egypt. 1 January 2024. Retrieved 1 January 2024.
- ↑ "Country Level". 2007 Population and Housing Census of Ethiopia. CSA. 13 July 2010. Archived from the original on 8 February 2019. Retrieved 18 January 2013.
- ↑ "Population Projection of Ethiopia for All Regions At Wereda Level from 2014 – 2017". Government of Ethiopia. Retrieved 20 April 2016.
Read further
- Campbell G, Miers S, Miller J (2007). Women and Slavery: Africa, the Indian Ocean world, and the medieval north Atlantic. Ohio University Press. ISBN 978-0-8214-1723-2.
- Cana FR, Gleichen AE (1911). "Abyssinia" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 1 (11th ed.). pp. 82–95.
- Deguefé, Taffara (2006). Minutes of an Ethiopian Century, Shama Books, Addis Ababa, ISBN 99944-0-003-7.
- Hugues Fontaine, Un Train en Afrique. African Train, Centre Français des Études Éthiopiennes / Shama Books. Édition bilingue français / anglais. Traduction : Yves-Marie Stranger. Postface : Jean-Christophe Belliard. Avec des photographies de Matthieu Germain Lambert et Pierre Javelot. Addis Abeba, 2012, ISBN 978-99944-867-1-7. English den French. UN TRAIN EN AFRIQUE
- Henze PB (2004). Layers of Time: A History of Ethiopia. Shama Books. ISBN 978-1-931253-28-4.
- Keller E (1991). Revolutionary Ethiopia From Empire to People's Republic. Indiana University Press. ISBN 978-0-253-20646-6.
- Marcus HG (1975). The Life and Times of Menelik II: Ethiopia, 1844–1913. Oxford: Clarendon. Reprint, Trenton, NJ: Red Sea, 1995. ISBN 1-56902-009-4.
- Marcus HG (2002). A History of Ethiopia (updated ed.). Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-22479-7.
- Mauri, Arnaldo (2010). Monetary developments and decolonization in Ethiopia, Acta Universitatis Danubius Œconomica, VI, n. 1/2010, pp. 5–16. Monetary Developments and Decolonization in Ethiopia and WP Monetary developments and decolonization in Ethiopia
- Mockler A (1984). Haile Selassie's War. Reprint, New York: Olive Branch, 2003 ISBN 0-902669-53-2.
- Murphy, Dervla (1968). In Ethiopia with a Mule. London: Century, 1984, cop. 1968. N.B.: An account of the author's travels in Ethiopia. 280 p., ill. with a b&w map. ISBN 0-7126-3044-9
- Rubenson S (2003). The Survival of Ethiopian Independence (4th ed.). Hollywood, CA: Tsehai. ISBN 978-0-9723172-7-6.
- Selassie I H (1999). My Life and Ethiopia's Progress: The Autobiography of Emperor Haile Selassie I. Translated by Edward Ullendorff. Chicago: Frontline. ISBN 978-0-948390-40-1.
- Siegbert Uhlig, et al. (eds.) (2003). Encyclopaedia Aethiopica, Vol. 1: A–C. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz Verlag.
- Siegbert Uhlig, et al. (eds.) (2005). Encyclopaedia Aethiopica, Vol. 2: D–Ha. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz Verlag.
- Siegbert Uhlig, et al. (eds.) (2007). Encyclopaedia Aethiopica, Vol. 3: He–N. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz Verlag.
- Siegbert Uhlig & Alessandro Bausi, et al. (eds.) (2010). Encyclopaedia Aethiopica, Vol. 4: O–X. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz Verlag.
- Alessandro Bausi & S. Uhlig, et al. (eds.) (2014). Encyclopaedia Aethiopica, Vol. 5: Y–Z and addenda, corrigenda, overview tables, maps and general index. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz Verlag.
- Zewde B (2001). A History of Modern Ethiopia, 1855–1991 (2nd ed.). Athens, OH: Ohio University Press. ISBN 978-0-8214-1440-8.
- Dis article dey incorporate text from dis source, wich edey insyd de public domain. Country Studies. Federal Research Division.
- Dis article dey incorporate public domain material from The World Factbook. CIA.
External links
Ethiopia at Wikipedia ein sisto projects
- Definitions from Wiktionary
- Media from Commons
- News from Wikinews
- Quotations from Wikiquote
- Texts from Wikisource
- Textbooks from Wikibooks
- Travel information from Wikivoyage
Scholia get topic profile give Ethiopia.
- Ethiopia. The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency.
- BBC Ethiopia Profile
- World Bank Ethiopia Summary Trade Statistics
- Ethiopia at Curlie
- Key Development Forecasts for Ethiopia from International Futures.
- Ethiopia pages – U.S. Dept. of State (wich dey include current State Dept. press releases den reports for Ethiopia top)
- Pages with script errors
- Articles using generic infobox
- Ethiopia
- East African countries
- Federal republics
- Horn African countries
- Landlocked countries
- Least developed countries
- Member states of de African Union
- Member states of de United Nations
- Countries for Africa insyd
- BRICS nations
- Pages using ISBN magic links
- Pages using the Kartographer extension

